Comprehensive Guide to Urinary Bladder Cancer Treatment
Urinary bladder cancer is one of the most common cancers, with treatment strategies evolving to enhance patient outcomes and quality of life. A personalized approach to treatment, considering the cancer stage, grade, and individual health factors, is crucial. This blog will provide a detailed look at the available treatment options.
Treatment Options for Urinary Bladder Cancer
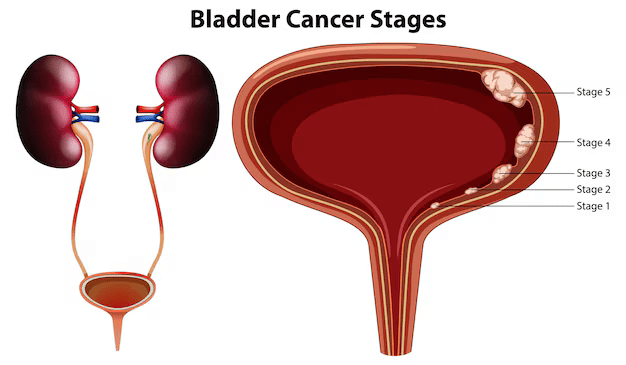
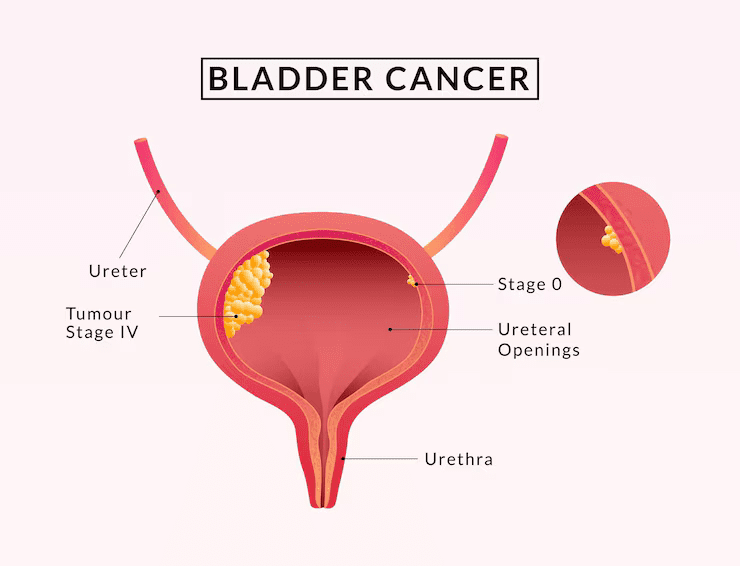
Bladder cancer treatment depends on its stage and grade. Here’s a quick overview:
1. Early-Stage (Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer):ood Nutrition Improves Well-Being
- TURBT: Removes tumors via a cystoscope.
- Intravesical Therapy: BCG immunotherapy or chemotherapy to prevent recurrence.
2. Advanced (Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer):
- Radical Cystectomy: Removes the bladder and reconstructs urinary pathways.
- Chemotherapy & Radiation: Shrink tumors or manage cancer post-surgery.
3. Metastatic Bladder Cancer:
- Systemic Chemotherapy: Platinum-based drugs like cisplatin.
- Immunotherapy: Checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., pembrolizumab).
- Targeted Therapy & Trials: For genetic mutations or novel approaches.
Types of Bladder Cancer
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC): The most common type, originating in the urothelial cells lining the bladder.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Linked to chronic irritation and infections.
- Adenocarcinoma: A rare type arising from glandular cells in the bladder.
Risk Factors
- Smoking: The most significant risk factor due to exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Exposure to Chemicals: Dyes, rubber, leather, or petroleum products.
- Chronic Bladder Infections: Prolonged irritation increases the risk.
- Radiation or Chemotherapy: Previous treatment for other cancers.
- Family History: Genetic predisposition.
Symptoms
- Blood in urine (hematuria) – the most common symptom.
- Frequent or painful urination.
- Urgency to urinate.
- Pelvic or back pain (in advanced stages).
Diagnosis
- Urinalysis: To detect blood or cancer cells in urine.
- Cystoscopy: A scope is inserted into the bladder to visualize the inner surface.
- Imaging Studies: CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound for tumor visualization.
- Biopsy: Tissue samples are taken for confirmation.
Treatment Options
Surgical Interventions:
- Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): For early-stage cancers.
- Radical Cystectomy: Removal of the entire bladder in advanced cases.
- Intravesical Therapy:
- BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin): Immunotherapy to prevent recurrence.
- Chemotherapy: Delivered directly into the bladder.
- Systemic Chemotherapy: For advanced or metastatic cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: As an adjunct or alternative to surgery.
- Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy: Recent advancements like checkpoint inhibitors.
Preventions
- Avoid Smoking: Reduce exposure to carcinogens.
- Stay Hydrated: Flush out toxins regularly.
- Use Protective Gear: If exposed to harmful chemicals at work.
- Regular Screening: Especially for high-risk individuals.